Spending time outdoors is refreshing, but prolonged sun exposure can be harmful. How can you protect yourself from UV rays while staying comfortable? The answer lies in UV-protection fabrics, an innovation in outdoor clothing.
UV-protection fabrics are specially designed textiles that block or absorb ultraviolet radiation, reducing skin exposure to harmful sun rays. They offer better protection than regular fabrics, making them ideal for outdoor activities like hiking, fishing, and sports.
Let’s explore how these fabrics work, which materials are best, and how they are made UV-resistant.
What is UV-Protection Fabric?
Not all fabrics provide the same level of sun protection. Some materials allow UV rays to pass through, while others are engineered to block them effectively.
UV-protection fabric is any textile treated or constructed to reduce UV radiation exposure, offering higher protection than standard clothing. This is often measured using the Ultraviolet Protection Factor (UPF)1 rating system.
Understanding UPF Ratings
UPF measures how much UV radiation a fabric allows to reach the skin. (UPF Ratings Source: NIH - National Library of Medicine)
| UPF Rating | UV Blocked | Protection Level |
|---|---|---|
| UPF 15-24 | 93.3-95.9% | Good |
| UPF 25-39 | 96.0-97.4% | Very Good |
| UPF 40-50+ | 97.5%+ | Excellent |
A UPF 50 fabric allows only 2% of UV rays to pass through, offering 98% protection, making it an excellent choice for outdoor clothing.
What is UV-Treated Fabric?
Not all fabrics naturally block UV rays. Some require additional treatments to enhance their sun protection capabilities.
UV-treated fabric is a textile that has been chemically or physically modified to improve its ability to absorb or reflect ultraviolet radiation. This treatment helps boost a fabric’s UPF rating, ensuring better sun protection.
Common UV Treatments for Fabrics
- Chemical UV Absorbers – Fabrics are treated with UV-blocking agents like titanium dioxide2 or zinc oxide3.
- UV-Reflective Coatings – Special coatings enhance the fabric’s ability to reflect UV radiation.
- Dye Additives – Certain dyes absorb UV light, reducing exposure to the skin.
- Fabric Blending – Mixing synthetic fibers like polyester with natural materials enhances UV resistance.
UV treatments are commonly applied to outdoor clothing, swimwear, and workwear designed for prolonged sun exposure.
Which Fabric is Best for UV Protection?
The effectiveness of UV-protection fabrics depends on factors like weave density, fiber type, color, and chemical treatments.
Best Natural & Synthetic Fabrics for UV Protection
| Fabric Type | UV Protection Level | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Polyester | High | Tightly woven, naturally UV-resistant |
| Nylon | High | Durable and often UV-treated |
| Wool | Medium to High | Absorbs UV rays naturally |
| Cotton (untreated) | Low | Loose weave allows UV penetration |
| Linen | Low | Lightweight but not UV-resistant |
| Blends (Poly-Cotton, Nylon-Spandex) | Medium to High | Can be treated for added UV protection |
Key Factors Affecting UV Protection
- Weave Density – Tightly woven fabrics block more UV rays.
- Color – Darker and more saturated colors absorb more UV radiation.
- Fabric Thickness – Heavier fabrics offer better protection.
- Moisture Content – Wet fabrics may lose UV-blocking ability.
For the best UV protection, polyester, nylon, and high-UPF treated fabrics are ideal choices.
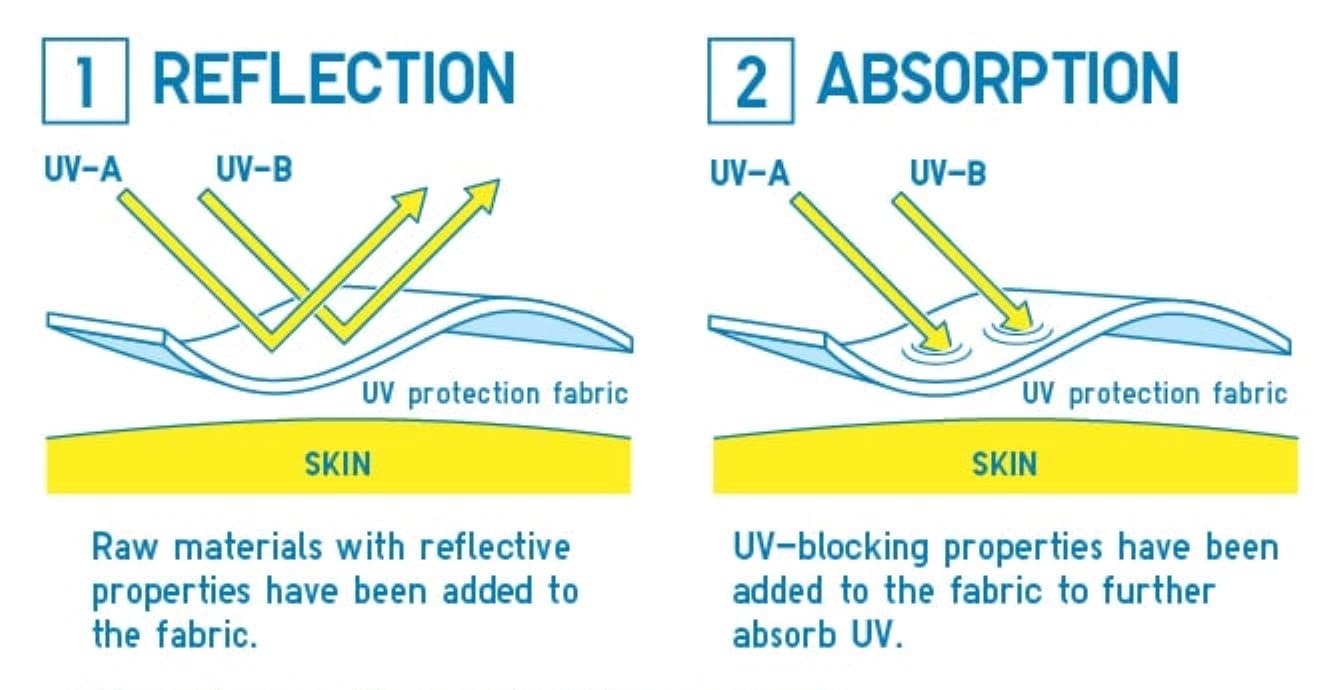
How Does UV Protection Fabric Work?
UV-protection fabric works by preventing harmful UV radiation from penetrating through the textile and reaching the skin.
How It Blocks UV Rays
- Absorption – Certain fabric fibers and dyes absorb UV rays before they reach the skin.
- Reflection – Some materials, like synthetic fibers, reflect a portion of the UV radiation away.
- Scattering – Special treatments create a surface that diffuses UV rays, reducing their impact.
Technology Used in UV-Protection Fabrics
| Technology | Function | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Titanium Dioxide & Zinc Oxide Treatments | Absorbs UV radiation | Activewear, sun hats |
| Microfiber Weaves | Dense structure blocks UV rays | Rash guards, fishing shirts |
| Moisture-Wicking UV Fabric | Keeps skin dry while blocking sun | Hiking & running gear |
These mechanisms ensure that UV-protection fabrics offer superior sun defense compared to untreated materials.
How Do We Make Fabric UV-Protected?
UV protection in fabrics can be achieved through both natural and chemical methods.
1. Weaving and Fiber Selection
- Tight Weaves – Less space between fibers means fewer UV rays penetrate.
- Synthetic Fibers – Polyester and nylon have built-in UV resistance.
2. UV-Blocking Chemical Treatments
Some fabrics are coated with UV-absorbing chemicals, such as:
- Titanium Dioxide – Commonly used in polyester fabrics.
- Zinc Oxide – Provides long-lasting UV resistance.
3. Dye and Color Enhancement
Dark or bright dyes improve UV absorption, reducing exposure.
4. Special Finishes and Coatings
- Moisture-Wicking & UV-Protective Coatings – Used in activewear.
- Water-Resistant Finishes – Help maintain UV protection even when wet.
By combining the right fibers, dyes, and treatments, manufacturers create fabrics that shield wearers from harmful UV rays.
Conclusion
UV-protection fabrics are essential for outdoor clothing, offering superior sun protection compared to regular textiles. Polyester, nylon, and tightly woven treated fabrics provide the best defense against harmful rays. Whether through fabric construction or chemical treatments, UV-resistant clothing helps prevent sunburn and long-term skin damage. When choosing outdoor apparel, always check for a high UPF rating to stay safe under the sun.
-
UPF (ultraviolet protection factor) represents the ratio of sunburn-causing UV without and with the protection of the fabric. ↩
-
Titanium dioxide, also known as titanium(IV) oxide or titania /taɪˈteɪniə/, is the inorganic compound derived from titanium with the chemical formula TiO2, sometimes referred to as TiO2, titanium white or CI 77891, it has been used for many years in a variety of different products including pharmaceuticals and cosmetics. ↩
-
Zinc oxide is an inorganic compound with the formula ZnO. It is a white powder which is insoluble in water. ZnO is used as an additive in numerous materials and products including cosmetics, food supplements, rubbers, plastics, ceramics, glass, cement, lubricants,[12] paints, sunscreens, ointments, adhesives, sealants, pigments, foods, batteries, ferrites, fire retardants, semi conductors,[13] and first-aid tapes. ↩