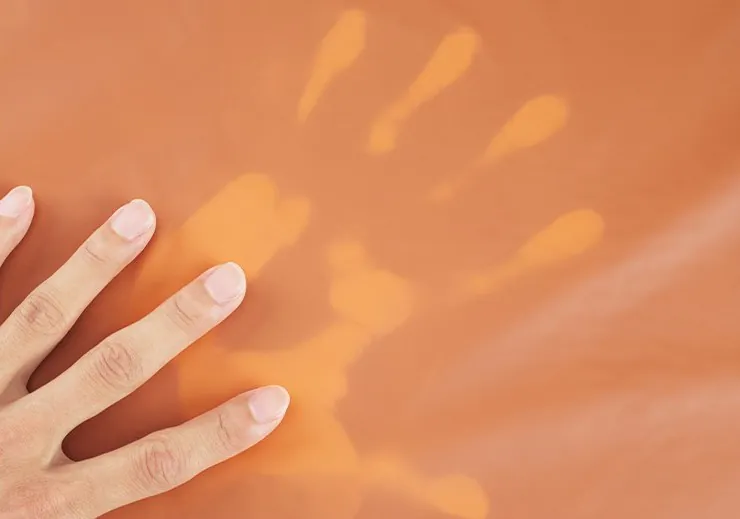
You see thermochromic fabric, aka heat sensitive fabric or heat reactive fabric, change when heat touches it. These color-changing fabrics use special pigments that switch color when the temperature changes. You notice the color change because the thermochromic dyes move when the fabric gets hot or cold. This color change makes the fabric lively and flexible, giving you a special experience each time you wear or use it.
Key Takeaways
Thermochromic fabric changes color when it gets hot or cold. This makes it fun and interactive for people to use. Special dyes and chemicals are inside the fabric. These react to temperature changes. This lets the fabric change color quickly. You can find thermochromic fabric in clothing and accessories. It is also used in safety gear. This makes things look cool and work better. It is important to take care of thermochromic fabric. Do not use bleach or high heat. This helps keep the color-changing effect strong. More people want thermochromic textiles now. New products will be in stores soon.
Thermochromic Fabric Basics

What Makes It Thermochromic
The secret of thermochromic fabric is in its chemicals. These fabrics have special dyes and compounds that react to heat or cold. When you touch the fabric or heat it up, the molecules move and the color changes. The most common dyes are spirolactones, fluorans, spiropyrans, and fulgides. There are also acids like bisphenol A and parabens that help control the reaction. All these chemicals are put inside tiny capsules. The capsules protect the chemicals and make the color change last longer.
Here is a table that shows the main chemicals in thermochromic fabrics:
Component | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
Dye | Organic | Molecules like spirolactones, fluorans, spiropyrans, and fulgides that change color with pH. |
Weak Acid | Acid | Proton donors like bisphenol A that influence the dye's color intensity and reversibility. |
Solvent | Polar Solvent | Typically alcohols or esters that are part of the microcapsule structure. |
These ingredients work together to make the fabric change color.
Key Features of Color-Changing Textiles
Color-changing textiles are special because they react to temperature. You see the color change right away when the fabric gets hot or cold. This quick reaction makes thermochromic materials different from other smart textiles. Other smart textiles might react to light or water, but thermochromic fabrics only need heat to work.
Tip: You can use thermochromic fabric in clothes, accessories, or sports gear for a fun effect.
Here is a table that compares thermochromic fabrics with other smart textiles:
Feature | Thermochromic Fabrics | Other Smart Textiles |
|---|---|---|
Mechanism | Change color with temperature variations | Respond to light, moisture, etc. |
Materials | Liquid crystals, leuco dyes | Various stimuli-responsive materials |
Applications | Military camouflage, sportswear, fashion | Varies widely across different textiles |
Color-changing textiles are exciting because they look different in different temperatures. The fabric changes with your environment and makes everyday things more interesting.
How Thermochromic Fabrics Work
Thermochromic Dyes and Pigments
There are two main types of color-changing textiles. One type uses leuco dyes. The other type uses liquid crystals. Both types use special dyes and pigments. These react when the temperature changes. They work in different ways to change color.
Thermochromism means the fabric can change color back and forth. When the temperature goes up or down, the color changes. When the temperature returns, the color goes back to normal.
Each dye or pigment has its own temperature for changing color. This is called the thermochromic transition temperature.
Some materials change color by moving their molecules. Others change because the liquid crystals shift their structure.
Liquid crystals are very sensitive to heat. When the temperature changes, their molecules move. This makes them reflect light in new ways. That is why the color shifts.
Here is how the molecules help the fabric change color:
Evidence | Description |
|---|---|
Electron transfer | The molecules change because electrons move at certain temperatures. This causes the color to change. |
Leuco dyes | Acids help the color change. For example, crystal violet lactone reacts with bisphenol-A. |
For example, crystal violet lactone and bisphenol-A react together. At low temperatures, the fabric stays clear. When it gets warmer, the lactone ring opens. Then you see a bright color.
Here is a table comparing leuco dye and liquid crystal textiles:
Feature | Leuco Dye | Liquid Crystal |
|---|---|---|
Mechanism | Chemical reaction | Molecules line up differently |
Color Change | Changes between two colors or clear | Shifts in rainbow-like colors |
Use Cases | Mood rings, mugs that change color | Medical thermometers, battery testers |
Pros | Easy to use, cheap, bends easily | Very accurate, changes fast |
Cons | Not as exact, works in fewer temperatures | Costs more, sensitive to sunlight and water |
Temperature Response Mechanism
You may wonder how the fabric knows when to change color. It is because of the temperature response mechanism. Each dye or pigment has a set temperature to activate. When the fabric reaches this temperature, the molecules move or react. This makes the color change.
Here is a table showing common activation temperatures:
Activation Temperature | Application |
|---|---|
15°C (59°F) | Cold places |
26°C (79°F) | Body heat |
31°C (88°F) | Warm drinks |
Some fabrics change color when you touch them. Others react to the air or things around them. The color change happens quickly. It can go back and forth as the temperature moves above or below the set point.
Thermochromic fabrics are different from other smart textiles. They only react to temperature. Photochromic fabrics react to sunlight instead. Thermochromic fabrics can change color in a wide range, from 30°C to 80°C. They keep working even after many uses. Photochromic fabrics may lose their color faster if used outside.
Fabric Type | Responsiveness | Durability |
|---|---|---|
Thermochromic | Changes color in a wide temperature range | Lasts a long time (slight fading after many washes) |
Photochromic | Reacts to sunlight | Loses color faster in the sun & air |
You can use thermochromic fabric for fun or for useful things. The science behind these fabrics makes them special and dependable for many uses.
Making Thermochromic and Programmable Color Changing Fabric
Materials and Technologies
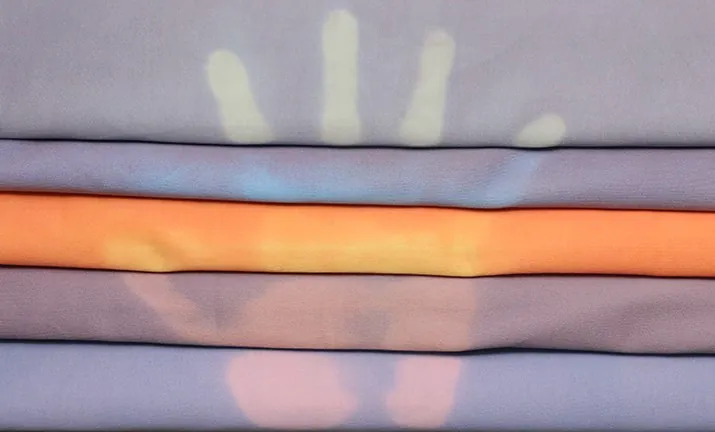

Modern thermochromic textiles use many different materials. These materials help the fabric change color with heat or electricity. The most common ones are thermochromic dye, thermochromic pigments, and special fibers. Some fabrics use heating wire to make the color change stronger. Cotton and other cellulose fibers work well for dyeing. Painting methods can be used on many types of fibers.
Here is a table that lists the main materials in programmable color changing fabric:
Material Type | Description |
|---|---|
Thermochromic Dyes | Dyes that change color when heated, sometimes turning clear. |
Thermochromic Pigments | Pigments that make bright colors, especially with acrylic gel. |
Fiber Types | Cotton and cellulose fibers are best for dyeing. |
Heating Wire | Thin magnet wire heats up to help the color change. |
New technology makes programmable color changing fabric even better. Some fabrics have tiny wires woven into the yarn. When you send electricity through these wires, the heat makes the thermochromic dye or pigment change color. Some fabrics have patterns you can control. This lets you pick which parts of the fabric change color. You get more choices for design and how the fabric works.
Technology | Description |
|---|---|
Conductive Micro-Wires | Use electric current to make pigments change color. |
Thermochromic Microcapsules | Change color with heat for cool effects. |
Programmable Patterns | Control groups of fibers to make different patterns. |
Manufacturing Process
Making thermochromic and heat reactive fabric is not like making regular fabric. Special steps are used to add heat activated thermochromic dye or pigment to the fibers. Some methods put the colorants inside tiny capsules and then into the yarn. Others use wet spinning to make yarn that changes color and can be woven into fabric. Scientists have made microcapsules using in situ polymerization. This helps the fabric keep its color-changing power for a long time.
Some companies use cholesterol liquid crystal microcapsules for strong thermochromic effects.
Others put the colorants inside the fiber so the fabric stays sensitive and stable for months.
Wet spinning makes yarn that keeps changing color even after thousands of times.
Programmable color changing fabric is a smart textile. You can control the color and pattern with heat or electricity. The fabric reacts fast to your touch or the air. It gives you a lively experience, not like regular fabric. You get style and function, like temperature control and fun designs, from these smart fabrics.
Tip: Programmable color changing fabric lets you make custom looks and show messages or patterns on your clothes!
Applications and Challenges of Color-Changing Textiles
Uses in Fashion and Novelty Products
You can find color-changing textiles in many clothes and fun items. T-shirts, hats, and shoes use thermochromic fabric for cool designs. The colors change with your body heat or the weather. These products make your style more fun and interactive. Some accessories change color when you touch them or go outside. People want more clothes that are interactive and can be customized. More brands now use smart fabric for new looks and experiences.
Color-changing textiles help you show your own style.
Your clothes react to the world around you.
The market is growing as people want more interactive fashion.
Industrial and Technological Applications
Color-changing textiles help keep people safe at work. Thermochromic labels on machines warn about dangerous heat. Food packages use these labels to show if food got too hot. Medical devices have stickers that change color with temperature. Firefighter gear and work clothes use special yarn to warn about high heat.
Application Area | Description |
|---|---|
Machinery | Labels warn about dangerous heat to stop accidents. |
Food Packaging | Labels show if food gets too hot and might spoil. |
Medical Devices | Stickers change color to warn about unsafe temperatures. |
Firefighter Equipment | Yarn helps check the temperature for safety. |
Industrial Clothing | Yarn warns workers if it gets too hot, keeping them safer. |
You also see these textiles in wearable tech for health. They can show if you have a fever or feel tired by changing color. Some socks and bandages use thermochromic dye to show temperature changes.
Durability and Usability Issues
There are some problems with color-changing textiles. The fabric may stop changing color after many washes or lots of use. Sometimes, the color does not change the same way every time. High heat can make the microcapsules not work as well. The pigments may not last as long as regular dyes in sunlight or heat.
Limitation | Description |
|---|---|
Durability | Does not last as long after many washes. |
Color Transition Performance | Color change may not be the same in every batch. |
Efficacy at High Temperature | Microcapsules do not work as well in high heat. |
Stability of Pigments | Pigments fade faster than normal dyes in light and heat. |
But research shows thermochromic fibers can still work after thousands of uses. You get good results if you follow the care instructions.
Care Instructions
You need to care for thermochromic fabric in a special way. Do not use bleach or dry with high heat. Do not iron right on the color-changing parts. These steps help keep the color-changing effect strong.
Fabric Type | Care Instructions |
|---|---|
Thermochromic Fabrics | Do not use bleach, high heat, or iron on the color-changing areas. |
Traditional Textiles | Usually do not need special care for heat or chemicals. |
Tip: Wash color-changing clothes gently and keep them away from strong chemicals to help them last longer.
You now know that thermochromic fabric changes color with heat. This cool technology makes clothes and other items more fun and helpful. It is used in fashion, safety gear, and health products. More products will come out as the market gets bigger.
The thermochromic pigment market will grow by about 15% each year from 2024 to 2035.
New ideas in textiles help this market grow.
You may soon see new styles and smart clothes in stores. Color-changing textiles might change what you wear and use in the future.
FAQ
What happens if you wash thermochromic fabric in hot water?
Hot water can damage the color-changing effect. You should wash thermochromic fabric in cold or lukewarm water. This helps the special dyes last longer.
Can you iron thermochromic clothing?
You should avoid ironing directly on the color-changing areas. High heat can ruin the pigments. If you need to iron, use a low setting and place a cloth over the fabric.
Does thermochromic fabric work outdoors?
Thermochromic fabric works outside, but sunlight and weather can fade the colors faster. You should store these items away from direct sunlight when not in use.
Is thermochromic fabric safe for skin contact?
You can wear thermochromic fabric safely. Manufacturers design these textiles for skin contact. The dyes stay inside the fibers and do not leak out.
How long does the color-changing effect last?
The color-changing effect lasts for many uses if you follow care instructions. Over time, washing and sunlight may reduce the brightness. Most fabrics keep working for months or years.