DWR fabric, or Durable Water Repellent fabric, is a type of material treated with a coating to make it water-resistant. While not completely waterproof, it is designed to repel water, keeping the fabric light and dry during outdoor activities. Over time, many outdoor apparel brands have adopted DWR treatments to enhance the functionality of clothing for hikers, climbers, and athletes. However, understanding its durability, safety, and maintenance is key to making the most of it.
DWR fabric refers to materials treated with a water-repellent coating, designed to keep you dry by causing water to bead and roll off rather than soak in.

Key Takeaways
-
DWR fabric means Durable Water Repellent fabric. It helps keep you dry by making water roll off.
-
DWR-treated fabrics are light and let air through. They are great for outdoor fun like hiking and camping.
-
Take care of your gear. Add more DWR coating when water stops rolling off to keep it working well.
-
Pick eco-friendly DWR types like C0 DWR. They protect nature while you enjoy outdoor activities.
-
DWR fabric is loved for outdoor gear. More people want eco-friendly and water-resistant products.
1. What is DWR Fabric?
DWR fabric stands for Durable Water Repellent fabric.
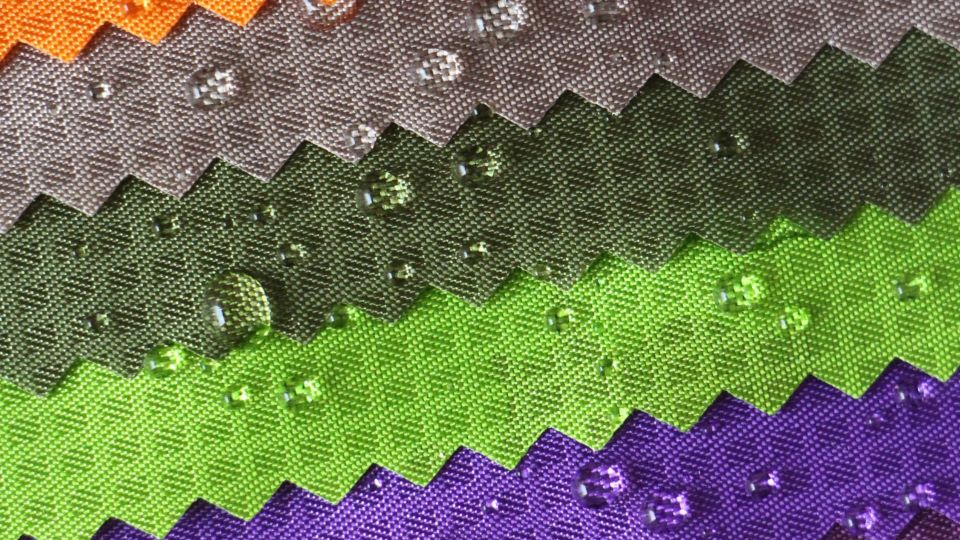

It has a thin coating that stops water from soaking in. Water forms drops and rolls off the surface instead.
This coating is typically made from fluoropolymers or newer eco-friendly alternativesc, creating a microscopic layer on the fabric’s surface that is hydrophobic (water-repellent). When water comes into contact with the treated fabric, it forms droplets due to the high surface tension, preventing it from spreading and soaking into the material. This is very helpful for outdoor gear like jackets or tents. It keeps you dry while hiking or camping.
The main goal of DWR is to repel water. The coating stops moisture from sticking to the fabric. This is important for outdoor clothes and gear, especially in wet weather.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Water Resistance | Makes water roll off, keeping you dry. |
| Stain Resistance | Helps repel stains, making cleaning easier. |
| Extended Lifespan | Protects fabric from water and stain damage. |
| UV Protection | Some coatings block harmful sun rays, great for hats or umbrellas. |
| Lifespan of DWR Coating | Good coatings last many seasons with care. |
| Resistance Levels | Different coatings handle various water pressure levels. |
Key features and benefits of DWR-treated materials
DWR-treated fabrics have many benefits. They repel water, so they don’t get soaked. This keeps your gear light and breathable, even in rain.
These fabrics also resist stains, making them easier to clean. You won’t need to wash them as often, which helps them last longer. Some DWR coatings even block UV rays, making them great for sunny days outdoors.
To keep DWR coatings working well, you need to maintain them. Dirt, oils, and washing can wear them out over time. Reapplying the coating brings back its water-repellent power, so your gear stays useful.
Common fabrics treated with DWR technology
DWR coatings are used on many outdoor fabrics. Synthetic materials like polyester and nylon are common. These are used for jackets, backpacks, and tents because they are light and strong.
Cotton blends can also get DWR treatments. This makes them water-resistant but still soft and comfy. High-tech fabrics like Gore-Tex often have DWR coatings to work better in wet weather.
Whether you’re hiking or walking in the rain, DWR-treated fabrics protect you. They are tough and useful, making them a must-have for outdoor gear.
How Does DWR Work?
The science behind DWR coatings
DWR coatings add a shield to fabric surfaces. This shield changes how water behaves on the fabric. Instead of soaking in, water turns into drops and rolls off. Scientists use special chemicals to make the surface water-repellent, or hydrophobic.
The secret is in the contact angle of water on the fabric. A contact angle shows if water spreads out or stays as drops. If the angle is over 90 degrees, the surface is hydrophobic. This means water barely touches the fabric, keeping it dry. Some surfaces, like lotus leaves, have angles over 170 degrees, making them super water-repellent. DWR coatings copy this natural trick to keep you dry.
Interaction of DWR with fabric surfaces
When DWR is added to fabric, it sticks to the fibers. This creates a barrier that stops water from soaking in. Water forms drops and slides off instead, leaving the fabric dry.
This works best on synthetic fabrics like nylon or polyester. These materials are smooth and light, so the coating spreads evenly. Natural fabrics like cotton may need extra treatments to work as well.
DWR coatings also let air pass through the fabric. This keeps you cool and comfy during outdoor fun. The mix of water resistance and breathability makes DWR-treated fabrics very useful.
Hydrophobic properties and their role in water repellency
Hydrophobic properties are what make DWR work. They stop water from soaking into the fabric. Instead, water forms drops and rolls away.
The contact angle decides how well this works. A higher angle means better water resistance. For example:
-
A contact angle over 90 degrees means the surface repels water.
-
A contact angle above 170 degrees makes the surface super water-repellent.
DWR coatings improve these properties by changing the fabric’s surface. This change lowers surface tension, so water can’t stick. This keeps your gear dry, even in rain.
Knowing how DWR works helps you see why it’s important. Whether hiking in rain or camping in wet weather, DWR-treated fabrics keep you dry and ready.
Application Process
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Spray Application | The coating is sprayed onto the fabric surface. |
| Padding | The fabric is passed through a bath of the chemical solution and then squeezed to remove excess liquid. |
| Curing | The treated fabric is heated to bond the coating to the fibers, ensuring durability. |
Applications and Limitations of DWR Fabric
Uses in outdoor clothing, gear, and accessories
DWR fabric is important for outdoor clothing and gear. It is used in jackets, backpacks, and tents. This fabric keeps you dry in light rain or damp weather. Unlike heavy waterproof clothes, DWR-treated items are light and let air through.
-
These fabrics work well for light outdoor activities without feeling heavy.
-
More people want DWR fabrics as companies make better designs for outdoor fun.
Whether hiking, camping, or walking in the rain, DWR gear is comfy and useful.
Performance limitations in extreme conditions
DWR fabric works well in mild weather but struggles in harsh conditions. Heavy rain or long exposure can make the fabric soak water. This lowers its breathability and water resistance.
Here’s a comparison of two common waterproof membranes used with DWR fabrics:
| Parameter | Gore-Tex | eVent |
|---|---|---|
| Breathability | 15,000–25,000 g/m²/24hr (RET ~6) | 30,000–40,000 g/m²/24hr (RET ~3) |
| Activation | Needs body heat | Quickly removes vapor |
| Durability | Very strong against wear | Slightly less due to no PU |
Both membranes are very waterproof, with hydrostatic heads over 28,000 mm. Gore-Tex lasts longer and keeps heat better, great for cold weather. eVent removes moisture faster, perfect for active sports like running.
Importance of the underlying fabric or membrane
The base fabric or membrane affects how DWR materials perform. The outer fabric, often nylon or blends, holds the DWR coating. This layer isn’t fully waterproof but helps water roll off while staying breathable.
-
The outer fabric protects the waterproof layer and helps DWR work well.
-
Good DWR stops the fabric from soaking water, called “wetting out.”
-
The membrane, usually made of ePTFE or polyurethane, blocks water even under pressure.
By mixing a strong outer fabric with a good membrane, companies make gear that is water-resistant, breathable, and tough. This keeps you comfy during outdoor adventures, even in tough weather.
Environmental Concerns and Sustainable Alternatives
Types of Chemical Coatings
| Aspect | Fluoropolymer-Based Coatings | Eco-Friendly Alternatives |
|---|---|---|
| Common Chemicals | Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) and Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS). | Fluorocarbon-free treatments, such as paraffin wax and silicone. |
| How It Works | Creates a durable, long-lasting water-repellent barrier. | Mimics the water-repellent properties of fluoropolymers without using harmful chemicals. |
| Pros | Highly effective, durable, and widely used in the outdoor industry. | More sustainable and environmentally friendly. |
| Cons | Not environmentally friendly; breaks down into harmful PFCs that persist in the environment. | May not be as durable or long-lasting as traditional fluoropolymer coatings. |
Problems with PFC-based DWR treatments
Old DWR coatings often use PFCs, which are harmful chemicals. These chemicals repel water well but hurt the environment. PFCs stay in soil and water for a long time, causing pollution. They can harm animals and even enter the food we eat, damaging ecosystems.
Buying items with PFC-based DWR can add to this problem. Many governments now limit or ban PFCs in fabrics to protect nature. Environmental groups also warn people about these dangers.
Is DWR toxic to humans?
DWR coatings have evolved significantly over time. Early treatments contained long-chain chemicals like PFOA(Perfluorooctanoic Acid) and PFOS(Perfluorooctane Sulfonate), which raised concerns about toxicity and environmental impact. Modern alternatives are less harmful, yet the topic remains a point of discussion for safety-conscious consumers.
Modern DWR treatments are considered safe for humans, but earlier versions with long-chain fluorochemicals posed health risks.
Breaking down the safety of DWR
- Fluorocarbon concerns: Many brands now use shorter-chain fluorochemicals or fluorine-free alternatives to reduce toxicity and environmental harm.
- Direct exposure: While exposure from wearing treated fabrics is minimal, applying sprays or washes without proper ventilation might pose risks.
- Environmental focus: Companies are increasingly shifting to sustainable options, but users should check product labels for safety certifications like bluesign® or OEKO-TEX®
DWR is safer than ever, but consumers should remain informed and prioritize brands committed to eco-friendly solutions.
Safer choices like C0 DWR
C0 DWR is a safer option that avoids harmful PFCs. It still keeps water away but uses better, non-toxic chemicals. This makes it safer for the planet.
You can find C0 DWR in jackets, bags, and other gear. These items work well in light rain and are eco-friendly. Choosing C0 DWR products helps the environment and supports green practices.
Industry shift to eco-friendly water repellents
The fabric industry is moving toward greener water-repellent options. People want eco-friendly products, and companies are creating better solutions. New nanotechnology makes sustainable DWR coatings stronger and more effective.
Here are some trends:
| Evidence | Description |
|---|---|
| Demand for outdoor apparel | More people want water-resistant clothes for outdoor fun. |
| Growing demand for sustainability | Shoppers choose eco-friendly fabrics to avoid harmful chemicals. |
| Regional leadership | Europe and North America lead in using bio-based DWR due to strict rules and awareness. |
| Rapid growth in Asia-Pacific | Countries like Japan and South Korea promote green textiles with government support. |
These trends show a big move toward eco-friendly solutions. Picking sustainable DWR items helps the planet and pushes the industry to improve.
How long does a DWR coating last?
DWR coatings don’t last forever, even on high-quality gear. Regular use, washing, and environmental exposure gradually reduce their effectiveness. You may notice water no longer beads on the fabric, signaling it's time for maintenance.
The lifespan of a DWR coating depends on usage and care, but most treatments last 6-12 months with proper washing and reproofing.
Modern DWR (Durable Water Repellent) treatments have become slightly less effective compared to those used over five years ago, as they have shifted to PFC-free formulas to address environmental concerns.
While these eco-friendly alternatives still provide water repellency, they tend to be less durable than the older, more toxic formulations that contained perfluorinated chemicals. This trade-off reflects the industry's effort to balance performance with sustainability.
Does DWR wash off?
Yes, DWR coatings degrade over time due to washing, abrasion, and environmental exposure. Washing with strong detergents or improper cleaning can significantly reduce its effectiveness.
DWR coatings do wash off eventually, especially without proper maintenance, but reproofing can restore water repellency.
Maintaining DWR-Treated Fabrics

Knowing when to reapply DWR treatment
Over time, DWR coatings wear out. Dirt and oils weaken them. Water stops forming drops and starts soaking in. To check, sprinkle water on the fabric. If it absorbs, you need to reapply the coating.
Reapply DWR coatings regularly to keep your gear waterproof. Washing or using a spray can restore its water-repellent power. This keeps your outdoor clothes ready for adventures.
Restoring DWR coatings
If water doesn’t bead up anymore, reapply the DWR coating. First, clean the fabric to remove dirt and oils. After drying, use a spray-on or wash-in product to bring back its water-repellent features.
Some people like spray-on treatments for small areas. Others prefer wash-in products for full coverage. Try both to see what works best for your gear. Reapplying often keeps your clothes ready for wet weather.
DWR fabric helps keep you dry and comfy outside. It repels water, making it great for jackets, tents, and gear. But, you need to care for it. Clean it often and reapply the coating to keep it working well.
When buying outdoor gear, look for eco-friendly DWR options. These choices are better for nature and still work great. Picking green products helps the Earth and gives you high-quality gear.
Extending the lifespan of DWR coatings
To maintain a DWR coating:
- Proper washing: Use mild detergents to avoid stripping the coating. Harsh cleaners can degrade its performance.
- Heat activation: Many DWR coatings can be revived by tumble drying on low heat or using an iron on a low setting.
- Reproofing products: Reapply DWR sprays or wash-in treatments designed for outdoor fabrics.
Understanding these steps ensures your gear remains water-repellent for a longer time. Regular maintenance can delay the need for reapplication and keep the fabric functioning like new.
Caring for DWR-treated fabrics
Taking care of DWR fabrics helps them last longer. Always read the care label before washing. Use mild soap made for outdoor gear, not regular detergent. Wash on a gentle cycle with warm water and rinse well.
Dry the fabric on low heat in a dryer. This spreads the coating evenly. If it’s still damp, let it air dry completely. These steps keep your gear breathable and water-resistant.
- Avoid harsh detergents: Use specific cleaners designed for outdoor gear. Harsh detergents can strip the coating.
- Follow care instructions: Check the garment tag for washing and drying guidelines.
- Reproof regularly: When water stops beading, use a reproofing product to restore the coating.
Tip: Don’t use bleach or fabric softeners. They harm the DWR coating and make it less effective.