Thermoplastic tape is a versatile material used for bonding and reinforcing fabrics. It solves the problem of weak or unprotected seams by providing durable and heat-activated adhesion.
Thermoplastic tape is a polymer-based adhesive material that melts when heated, bonding tightly to fabrics or surfaces to provide waterproofing, reinforcement, or structural stability.

This article explores its uses, related materials like thermoplastic sheets, and examples of thermoplastic applications.
What is thermoplastic tape used for?
Thermoplastic tape has many industrial and commercial applications, particularly in textile and construction industries. It addresses challenges like weak seams and fabric damage in harsh environments.
Thermoplastic tape is primarily used to seal seams, reinforce materials, and add structural integrity to fabrics and composites. It is often applied in waterproof garments, outdoor equipment, and aerospace components.
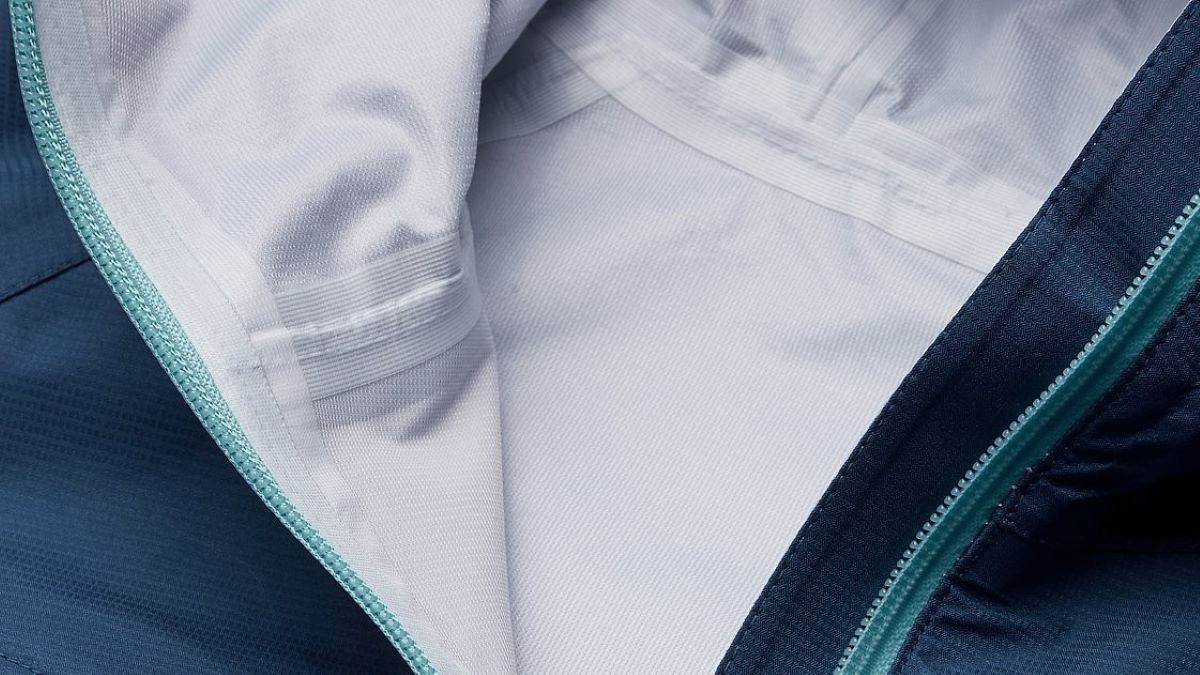

Key uses of thermoplastic tape
- Seam sealing1: Prevents water from penetrating stitched fabric seams.
- Reinforcement: Adds strength to lightweight materials.
- Composite bonding: Used in high-performance composites for aircraft and vehicles.
- Repair: Provides an efficient method for patching damaged areas.
Why is thermoplastic tape important?
Thermoplastic tape enhances durability without adding significant weight. For instance, in outdoor clothing, it ensures waterproof performance while maintaining fabric flexibility. In construction, it strengthens joints and connections, ensuring reliability.
Comparison with other sealing methods
| Feature | Thermoplastic Tape | Traditional Adhesives |
|---|---|---|
| Activation method | Heat | Chemical or pressure-based |
| Durability | High | Moderate |
| Flexibility | Retained after bonding | May become stiff or brittle |
Thermoplastic tape’s efficiency and adaptability make it indispensable for various industries.
What is thermoplastic sheet used for?
Thermoplastic sheets are large, flat polymer-based materials that serve as structural or functional components in a wide range of products. They solve the issue of rigid or inflexible materials by offering moldability and versatility.
Thermoplastic sheets are used in applications like protective barriers, medical devices, packaging, and automotive interiors, thanks to their durability, heat resistance, and lightweight nature.
How thermoplastic sheets work
Thermoplastic sheets become pliable when heated and harden upon cooling. This property allows them to be molded into various shapes and forms, making them ideal for complex designs.
Key applications of thermoplastic sheets
- Construction: Used as vapor barriers, roofing membranes, or wall panels.
- Healthcare: Formed into medical trays, prosthetic devices, or packaging.
- Automotive: Molded into dashboards, interior trims, or protective linings.
- Aerospace: Used in lightweight and heat-resistant components.
Advantages over traditional materials
| Feature | Thermoplastic Sheets | Traditional Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier |
| Recyclability | High | Low or none |
| Heat resistance | Adjustable | Fixed |
Thermoplastic sheets combine flexibility with durability, offering solutions for both practical and aesthetic requirements in modern industries.
What is an example of a thermoplastic?
Thermoplastics are an extensive class of polymers with diverse applications. One common example is polyethylene (PE), which is widely used for its strength, flexibility, and chemical resistance.
Polyethylene is a thermoplastic used in items like plastic bags, containers, and water pipes. It softens when heated, making it moldable and easy to process.
Other examples of thermoplastics
- Polypropylene (PP): Used in food packaging, textiles, and automotive components.
- Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC): Common in pipes, vinyl flooring, and medical equipment.
- Polycarbonate (PC): Utilized for its transparency and impact resistance in eyewear lenses and bulletproof glass.
Characteristics of thermoplastics
- Recyclable: Can be remelted and reused.
- Versatile: Suitable for a range of products, from flexible to rigid.
- Cost-effective: Mass production lowers manufacturing costs.
Comparison of thermoplastics
| Thermoplastic | Properties | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Polyethylene (PE) | Flexible, durable | Packaging, piping |
| Polypropylene (PP) | High chemical resistance | Automotive, textiles |
| Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | Strong, weather-resistant | Construction, medical devices |
Understanding these materials highlights their importance in everyday products and industrial applications.
Conclusion
Thermoplastic tape and sheets offer innovative solutions across industries by providing durable, heat-activated bonding and flexibility. From waterproof seams to molded parts, thermoplastics like polyethylene and polypropylene demonstrate their value in diverse applications.
-
Discover how Thermoplastic Tape work for waterproof seam sealing in outdoor jackets. ↩